Introduction
The transition to renewable energy is increasingly underscored by the pivotal role of solar farms, which serve as large-scale installations designed to convert sunlight into electricity. These facilities utilize advanced technologies such as photovoltaic (PV) panels and concentrated solar power (CSP) systems, enabling them to contribute significantly to the energy grid or cater to local consumption needs.
As the demand for solar energy surges, driven by both economic incentives and environmental imperatives, understanding the operational dynamics of solar farms becomes essential for stakeholders. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of solar farms, including:
- Their functionality
- Land leasing opportunities for landowners
- Economic benefits
- Environmental regulations
- Emerging trends that promise to shape the future of solar energy development
Through a comprehensive examination of these elements, readers will gain valuable insights into how solar farms are not only transforming the energy landscape but also offering substantial advantages to landowners and communities alike.
Understanding Solar Farms: Definition and Functionality
Solar installations represent a vital element in the shift to renewable sources, operating as large-scale setups that capture sunlight to generate electricity. These facilities primarily utilize photovoltaic (PV) panels or concentrated power (CSP) systems to transform energy from the sun into electrical power. The produced electricity can either be incorporated into the grid or used for local consumption, depending on the design and purpose of the facility.
The size of renewable energy farms can vary significantly, ranging from modest community projects to expansive utility-scale installations that can cover hundreds of acres, with average sizes differing by region. For example, in the U.S., the rising demand for renewable power has resulted in significant growth in module imports, with nearly 18 GW noted in Q2 2024, representing a 17% rise from the prior quarter. This trend demonstrates the increasing significance of sunlight power in the national power framework.
According to BNEF, installations from sunlight sources are anticipated to increase to 574 GW in 2024—29% above the additions of 444 GW forecasted for 2023—emphasizing the momentum behind renewable power development. Furthermore, the Low-Biomass Clean Power System case study in the UK illustrates the viability of inventive photovoltaic designs that correspond with clean energy objectives. Grasping the operational dynamics of photovoltaic farms is crucial for effective solar farm land services, which encompass essential aspects such as:
- Site selection
- Land leasing
- Adherence to regulatory compliance
It's important to note that estimates of installed renewable energy capacity may vary due to differences in reporting standards between DC and AC capacities. As photovoltaic capacity continues to evolve, stakeholders must stay informed about the functionality and design of installations to maximize their potential in contributing to clean power objectives.
Exploring Solar Farm Land Services: Leasing and Benefits for Landowners
Solar farm land services encompass a variety of activities focused on leasing property for energy projects, providing significant benefits for property owners. At present, the average lease cost for an acre of property in Delaware is $21.20, demonstrating the profitable potential of leasing for energy generation. As pointed out by David Muth from Peoples Company Capital Markets, what you’re having here is the energy lease rates that are multiples of the current cash rent rates.
This disparity emphasizes the financial motivation for property owners to contemplate renting their territory for solar farm land services related to renewable energy projects. However, it's essential to recognize that this rental data does not account for variations in available property, agricultural economy, or other lease terms, which can affect the fairness of rental costs. By entering into long-term lease agreements for solar farm land services, typically spanning several years, landowners can secure a steady stream of rental income that enhances their financial stability.
Additionally, insights from case studies, such as those on farmland rental values in Wisconsin, reveal that local demand and supply conditions significantly influence lease negotiations. Therefore, understanding these factors can provide a more nuanced view of the leasing landscape. Furthermore, renewable energy developers often invest in land improvements, such as better access roads and infrastructure upgrades, which can increase the overall value of the property.
Comprehending the leasing procedure, including negotiations and particular contract terms, is crucial for landowners interested in energy projects. The advantages go beyond quick monetary rewards; the new ecosystem created beneath the panels supports various plant and animal life, providing natural drainage and stormwater capture, thus enhancing environmental sustainability.
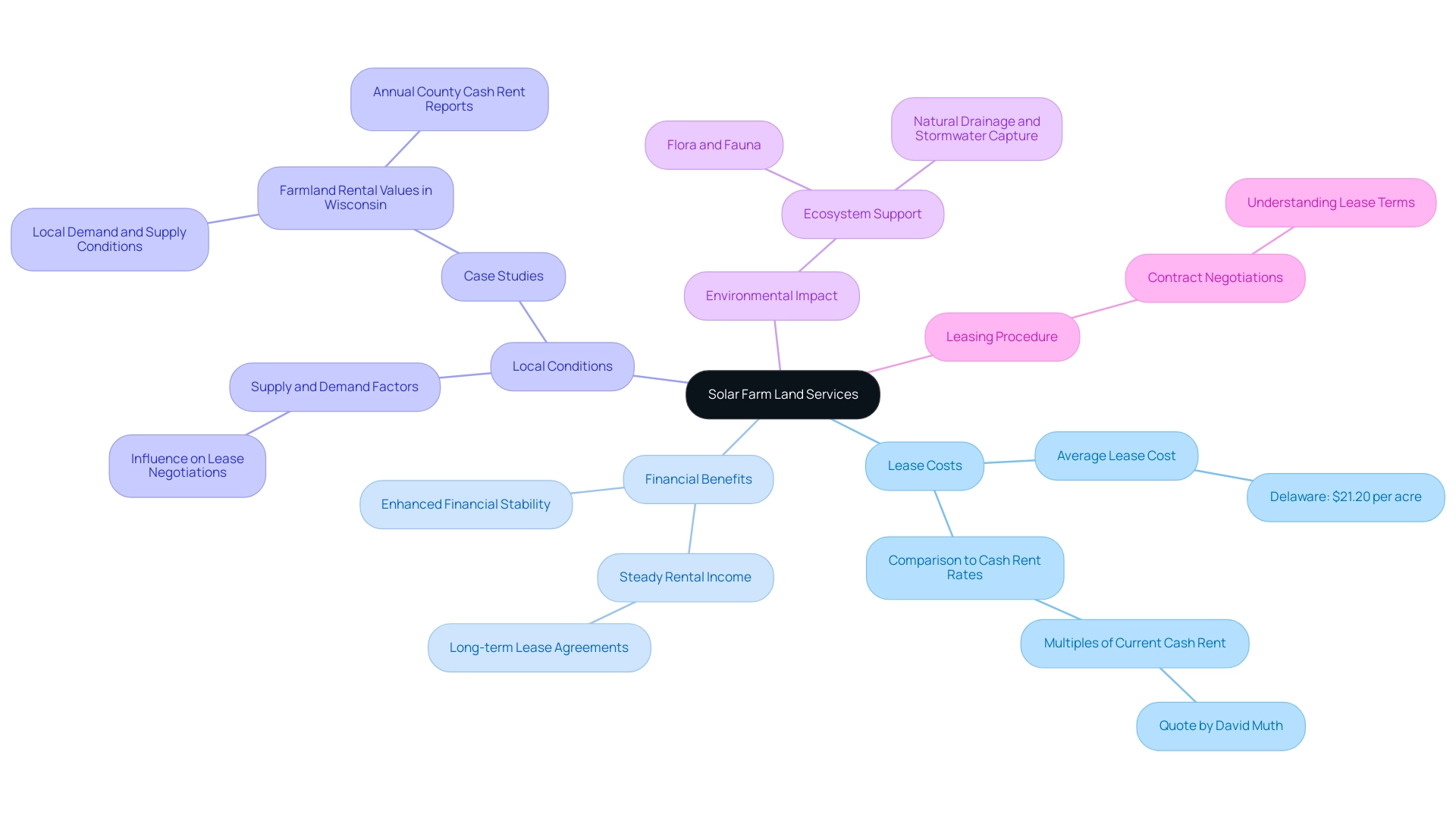
Economic Benefits of Leasing Land for Solar Farms
Leasing land for solar farm land services offers landowners a variety of substantial economic benefits. Typically, lease payments for photovoltaic installations can vary significantly, ranging from several hundred to several thousand dollars per acre annually, contingent upon factors such as location and the scale of the project. Significantly, numerous landowners also obtain extra payments linked to production or performance metrics, creating a chance for even higher financial returns.
This income stability is especially advantageous in rural areas, where traditional agricultural revenues can be unpredictable. Moreover, involvement in renewable projects such as solar farm land services may make landowners eligible for various tax benefits and grants linked to sustainable initiatives, thus improving the overall financial feasibility of leasing agreements. It is essential for landowners to consider minimum requirements for leasing, which include:
- Owning land free and clear
- A minimum size of 160 usable acres
- Zoning for utility use or farming
As emphasized by David Muth of Peoples Company Capital Markets, lease rates for renewable energy can significantly exceed current cash rent rates, reflecting the shifting economic landscape as such projects become more prevalent. The anticipated $63 million in payments from utility-scale renewable energy projects in Ohio's Brown County exemplifies the positive impact of these ventures on local economies. Additionally, the case study titled 'Trends in Farmland Market' indicates that farmland values have softened, prompting stakeholders to reassess their strategies amidst changing economic conditions.
Companies such as Shasta Power also play a crucial role in providing solar farm land services that assist landowners in maximizing property value while supporting the environment, making renewable energy projects an appealing choice for landowners aiming to improve their financial outlook.
Environmental Considerations and Regulations in Solar Farm Development
The establishment of solar farm land services is governed by a range of environmental regulations designed to safeguard local ecosystems and promote sustainable practices. Before starting construction, developers must perform environmental impact assessments (EIAs), which assess potential effects on wildlife, use of terrain, and water resources. These assessments are critical in identifying necessary mitigation strategies to reduce environmental harm.
Additionally, developers must adhere to local zoning laws and secure permits, often necessitating public consultations to foster community engagement. For instance, in Louisiana, agricultural land must encompass at least 3 acres or demonstrate an income of $2,000 from agricultural activities over the past four years to determine its use value. This regulatory framework is further supported by NY Energy, Art. 6, which establishes a state resource planning board responsible for forecasting power supply and demand, providing a broader context for renewable farm development. Furthermore, the CA Pub Util Code § 2854 (2019) requires local publicly owned electric utilities to implement initiatives for harnessing sunlight, supporting the expansion of residential and commercial systems. The Connecticut Gen. Stat. § 1-1 also offers legal definitions for 'agriculture' and 'farming' as mentioned in statutes related to power, enhancing the legal structure surrounding agricultural usage in renewable projects.
Such considerations are vital for landowners, as compliance with regulatory frameworks related to solar farm land services can significantly influence project timelines and lead to alterations in land use. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that approximately 90% to 97% of power materials are recyclable, as highlighted by expert Barry Elad, which underscores the long-term sustainability of energy initiatives.
Comprehending these environmental elements is crucial for efficiently managing the intricacies of renewable energy site development.
The Future of Solar Farm Land Services: Trends and Innovations
The changing environment of solar farm land services is expected to be influenced by a range of new trends and technological advancements. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing site selection processes, significantly enhancing the efficiency of property acquisition. For example, predictive analytics can pinpoint ideal sites for panel installations, reducing expenses and enhancing power output.
Simultaneously, the trend towards sustainable practices is driving the emergence of dual-use energy farms, where space is effectively utilized for both energy production and agricultural activities. This innovative approach not only optimizes land use but also creates additional revenue streams for landowners, thereby promoting economic sustainability. As Euan Graham, an Electricity and Data Analyst at Ember, noted, last year marked a significant change in power deployment, particularly in emerging markets such as the Philippines, UAE, Thailand, and Oman, which are increasingly importing panels.
This shift is further underscored by a notable 41% expected drop in California's residential energy volumes compared to 2023, highlighting contrasting dynamics within the market. Additionally, data on Chinese energy exports suggests strong growth in new markets, with countries like Pakistan and Saudi Arabia significantly increasing their panel imports. If these imports are installed, Pakistan and Saudi Arabia could join the ranks of established markets for sunlight energy, indicating a significant shift in global dynamics.
Staying informed about advancements in solar farm land services will be crucial for landowners and stakeholders involved in solar projects, ensuring they maximize the benefits of these developments.
Conclusion
Solar farms play a vital role in the transition to renewable energy, serving as large-scale installations that convert sunlight into electricity. The rise of photovoltaic and concentrated solar power technologies reflects the increasing importance of solar energy, bolstered by significant growth in capacity and imports.
For landowners, leasing land for solar projects offers substantial economic benefits, including:
- Attractive lease payments that exceed traditional agricultural rents.
- Long-term lease agreements that provide a steady income stream and enhance property value through improvements made by solar developers.
- Participation in these projects that can lead to tax incentives and grants, further improving financial viability.
Environmental regulations are essential in guiding solar farm development, ensuring sustainable practices while protecting local ecosystems. Awareness of these regulations is key for effective land management. The recyclability of solar materials underscores the sustainability of solar energy initiatives.
Emerging trends, such as the use of artificial intelligence for site selection and the development of dual-use solar farms, are set to reshape the industry. These innovations optimize land use and create additional revenue opportunities for landowners.
In summary, solar farms are transforming the energy sector, providing significant advantages to landowners and communities alike. As the demand for renewable energy increases, understanding the operational dynamics, economic benefits, and regulatory environments of solar farms will be crucial for stakeholders. Embracing these advancements will foster a sustainable and prosperous future for all involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are solar installations and how do they work?
Solar installations are large-scale setups that capture sunlight to generate electricity, primarily using photovoltaic (PV) panels or concentrated power (CSP) systems. The electricity produced can be integrated into the grid or used for local consumption, depending on the facility's design and purpose.
How do the sizes of solar energy farms vary?
The sizes of renewable energy farms can range from small community projects to large utility-scale installations covering hundreds of acres. Average sizes can differ by region.
What recent trends have been observed in solar module imports in the U.S.?
In Q2 2024, the U.S. saw significant growth in solar module imports, with nearly 18 GW recorded, marking a 17% increase from the previous quarter. This indicates the growing importance of solar power in the national energy framework.
What is the forecast for solar installations in 2024?
According to BNEF, solar installations are expected to increase to 574 GW in 2024, which is 29% higher than the 444 GW forecasted for 2023, highlighting the ongoing momentum in renewable energy development.
What are some essential aspects of solar farm land services?
Key aspects of solar farm land services include site selection, land leasing, and adherence to regulatory compliance.
How does the average lease cost for solar farm land compare to traditional cash rent rates?
The average lease cost for an acre of property in Delaware is $21.20, which is significantly higher than current cash rent rates, indicating a financial incentive for property owners to consider leasing for solar energy projects.
What factors can affect the fairness of rental costs for solar farm land?
Rental data may vary due to differences in available property, agricultural economy, and other lease terms, which can influence the fairness of rental costs.
What long-term benefits do landowners gain from leasing their land for solar projects?
By entering into long-term lease agreements for solar farm land services, landowners can secure a steady stream of rental income, enhancing their financial stability.
How do local demand and supply conditions impact lease negotiations?
Insights from case studies, such as those on farmland rental values in Wisconsin, show that local demand and supply conditions significantly influence lease negotiations, affecting rental agreements.
What additional investments do renewable energy developers often make on leased land?
Renewable energy developers frequently invest in land improvements, such as better access roads and infrastructure upgrades, which can increase the overall property value.
What ecological benefits can arise from solar farm land services?
The ecosystem created beneath solar panels can support various plant and animal life, providing natural drainage and stormwater capture, thereby enhancing environmental sustainability.
List of Sources
- Understanding Solar Farms: Definition and Functionality
- Quarterly Solar Industry Update (https://energy.gov/eere/solar/quarterly-solar-industry-update)
- ember-energy.org (https://ember-energy.org/latest-insights/solar-power-continues-to-surge-in-2024)
- Exploring Solar Farm Land Services: Leasing and Benefits for Landowners
- How Much do Solar Companies Pay to Lease Land in 2024? (https://smartenergyusa.com/how-much-do-solar-companies-pay-to-lease-land)
- Farmers Are Now Being Offered $1,000 Per Acre or More to Lease Their Land For Solar (https://agweb.com/news/business/taxes-and-finance/farmers-are-now-being-offered-1-000-acre-or-more-lease-their-land-solar)
- Land leasing for renewable energy | Landowner partnerships with Lightsource bp (https://lightsourcebp.com/us/partner-with-us/landowners)
- Farmland Rental Values in Wisconsin (https://farms.extension.wisc.edu/topics/pricing-and-contracts/land-lease-and-rental/farmland-rental-values)
- Economic Benefits of Leasing Land for Solar Farms
- Advantages and Challenges of Leasing Your Land for Solar (https://shastapower.com/sun-powered-income-the-advantages-and-challenges-of-leasing-your-land-for-solar)
- Farmers Are Now Being Offered $1,000 Per Acre or More to Lease Their Land For Solar (https://agweb.com/news/business/taxes-and-finance/farmers-are-now-being-offered-1-000-acre-or-more-lease-their-land-solar)
- How Leasing Your Land for a Solar Farm Can Boost Property Value - Shasta Power (https://shastapower.com/how-leasing-your-land-for-a-solar-farm-can-boost-property-value)
- Environmental Considerations and Regulations in Solar Farm Development
- Farmland Solar Policy State Law Database (https://farmandenergyinitiative.org/projects/farmland-solar-policy/state-law-database)
- Solar Energy Statistics and Facts 2024 (https://electroiq.com/stats/solar-energy-statistics)
- The Future of Solar Farm Land Services: Trends and Innovations
- ember-energy.org (https://ember-energy.org/latest-insights/solar-power-continues-to-surge-in-2024)
- Solar Market Insight Report Q3 2024 – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-market-insight-report-q3-2024)




