Overview
Community energy development refers to initiatives that empower local populations to produce and manage renewable energy resources, thereby enhancing sustainability and reducing dependence on external suppliers. The article outlines how these initiatives not only address economic and environmental challenges specific to communities but also promote job creation and social collaboration, illustrating their crucial role in advancing sustainable development in the face of increasing energy demands and climate impacts.
Introduction
In recent years, community energy development has emerged as a pivotal strategy for fostering local resilience and sustainability. This approach empowers communities to harness renewable energy resources, such as solar, wind, and biomass, thereby reducing reliance on external energy suppliers and addressing unique economic and environmental challenges.
With the rapid installation of renewable projects—one solar initiative launched every 39 seconds in 2023—communities are beginning to realize the substantial benefits of localized energy generation, including job creation and economic stimulation.
However, the path to successful community energy initiatives is not without obstacles, from regulatory complexities to funding barriers.
This article delves into the multifaceted landscape of community energy development, exploring its benefits, diverse models, challenges, and future trends, ultimately highlighting its crucial role in the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Defining Community Energy Development: An Overview
Community energy development includes initiatives that enable populations to produce, manage, and utilize power resources sustainably. This model primarily emphasizes renewable power sources, including solar, wind, and biomass, aiming to strengthen community resilience and support community energy development while reducing reliance on external suppliers. By placing management of power resources in the hands of the local population, community energy development initiatives tackle substantial economic and environmental issues unique to their geographic regions, ultimately advancing sustainable development.
For example, the most recent trends suggest a rise in regional renewable initiatives, with a significant figure revealing that a new solar project is set up every 39 seconds in 2023. As more groups participate in such initiatives, the potential for beneficial effects on regional economies becomes clear, encouraging job creation and boosting nearby investment. However, the challenges highlighted in case studies such as 'Future of Heat Pump Sales' reveal the contraction in heat pump sales in key markets, emphasizing the need for consistent policy support and alternative business models to enhance renewable heat deployment.
Moreover, the prediction for community energy development initiatives in 2024 indicates a sustained focus on strengthening neighborhoods, which is essential considering the anticipated increase in total heat-related emissions expected to surpass 100 Gt CO by 2030. This highlights the urgent need for enhanced renewable heat deployment and the role community initiatives play in mitigating climate impacts, particularly as cumulative heat-related emissions are projected to climb 4% by 2030.
The Benefits of Community Energy Initiatives for Local Communities
Collective power projects are a form of community energy development that offers numerous advantages for nearby populations, promoting economic development, generating employment, and encouraging environmental sustainability. By directing funding into regional resource systems, areas can greatly improve their retention of revenue related to resources, thus boosting local economies. Significantly, community energy development initiatives generate green employment in the installation, maintenance, and management of power systems, positioning neighborhoods as active participants in the transition to sustainable resources.
Furthermore, programs designed to incentivize community energy development have allocated substantial capacity—700 megawatts for low-income areas and 200 megawatts for Indian lands—demonstrating a commitment to equitable access to power, including those targeting low-income and Tribal communities. As Secretary Janet Yellen stated, "Investment in underserved people and places can lead to disproportionately higher rates of return for the nation’s economy." This investment is further illustrated by the minimum 20% bill credit discount for low-income households from eligible initiatives, which ensures that the financial advantages of clean solutions are distributed widely among residents.
These initiatives not only lessen greenhouse gas emissions and improve efficiency, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts, but they also promote community energy development by fostering collaboration among residents and local organizations. This improved cooperation fortifies social connections, ensuring that the economic advantages of renewable initiatives are distributed widely among residents, especially those in low-income households who stand to benefit from these discounts. The ripple effects of community energy development initiatives extend beyond simple economic measures; they represent a route toward a more sustainable and inclusive future.
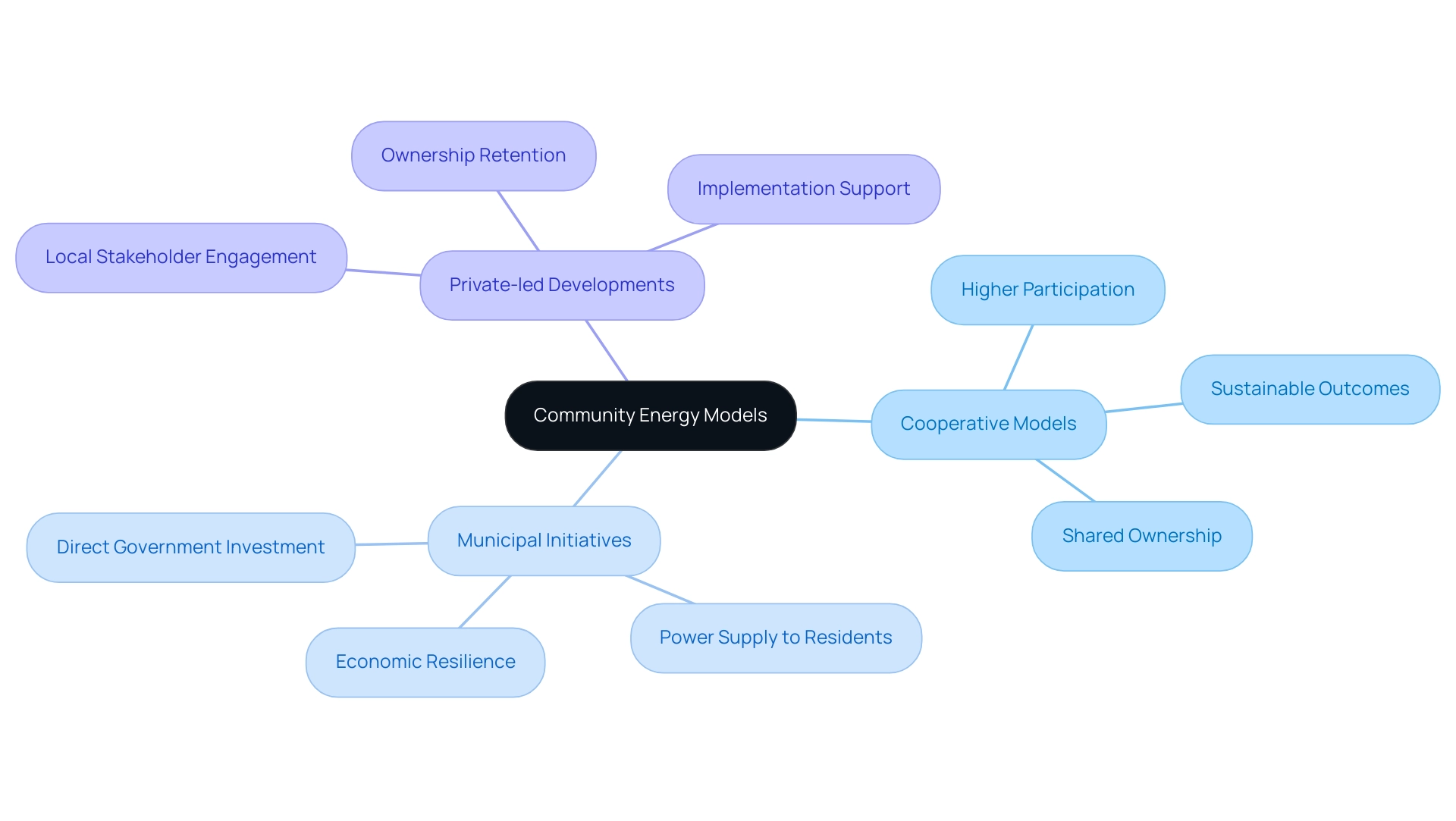
Exploring Different Models of Community Energy Projects
Different forms of community energy development can be observed, notably:
- Cooperative models
- Municipal initiatives
- Private-led developments
Collaborative models support community energy development by enabling community members to jointly possess and oversee renewable resources, such as solar farms, promoting community involvement and shared advantages. In contrast, municipal initiatives involve regional governments directly investing in renewable energy endeavors, contributing to community energy development while supplying power to residents and enhancing community economic resilience.
Private-led developments often engage local stakeholders during the planning and implementation phases to support community energy development while retaining ownership of the initiatives. Each approach presents distinct advantages and challenges. For example, cooperative models have demonstrated higher success rates in fostering participation and achieving sustainable outcomes.
Recent statistics indicate a significant growth trend in projects led by citizens, exemplified by the increase in EV charging stations in Germany, which rose from 28 to 209 over the past five years. This diversification in local power strategies enables residents to choose models that match their specific objectives and capabilities, ultimately advancing community energy development and progress toward a sustainable future. As highlighted by specialists, the solar market is expected to triple in size by 2028, emphasizing the crucial role of community energy development initiatives in the wider transition.
Valeria Jana Schwanitz emphasizes that while significant for individual countries, the contributions of citizens across Europe are crucial for community energy development and the overall transition. Furthermore, a suggested solar initiative in Arizona has been assessed, indicating possible economic contributions of around $4.8 billion to the state's gross domestic product and the generation of more than 50,000 job years of employment over 35 years, emphasizing the concrete advantages of collaborative power models.
Challenges and Keys to Success in Community Energy Development
Community energy development faces numerous obstacles, including regulatory barriers, funding limitations, and matters concerning public involvement. As organizations strive to meet sustainability goals, a notable 72% of respondents in a Deloitte survey indicate that they have strategies in place to assist in reducing carbon emissions. The financial environment for local energy initiatives is poised to enhance with the Inflation Reduction Act’s Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund, which is anticipated to offer $27 billion starting in 2024.
However, navigating the complex legal requirements inherent in these endeavors can significantly delay timelines. Securing adequate financing remains a critical barrier; many initiatives struggle to attract the necessary funding to move forward. Moreover, encouraging support from residents is crucial for the viability of community energy development; without regional buy-in, efforts risk failing to gain traction.
Successful local initiatives in community energy development rely on several key factors, including:
- Thorough stakeholder involvement
- Transparent communication
- Strategic use of regional resources and expertise
Moreover, adaptability and resilience in overcoming obstacles are essential traits of effective initiatives. The interconnection difficulties for clean power initiatives illustrate this point, as current regulations hinder their connection to the grid.
FERC's Order No. 2023 aims to improve interconnection wait times by transitioning to a 'first-ready, first-served' process, yet questions remain regarding its effectiveness in reducing delays. Furthermore, the restricted expansion of solar thermal capacity and the decline of heat pump sales underscore the urgent requirement for stable policy backing, which is essential for the success of community energy development.
Ultimately, utilizing robust local ties and creative financing methods will be essential in promoting successful power initiatives.
Future Trends in Community Energy Development
The future of community energy development is poised for substantial expansion and innovation, driven by swift technological progress and the changing power landscape. Current trends indicate a marked increase in the adoption of power storage solutions, with residential solar attachment rates projected to rise from 14% in 2023 to an unprecedented 25% in 2024, as noted by Thomas L. Keefe, Vice Chair and US Power, Utilities and Renewables Leader at Deloitte & Touche LLP. This surge reflects the broader shift towards decentralized power systems and smart grid technologies that are transforming community energy development in how neighborhoods manage their resources.
Moreover, the financial viability of local initiatives is underscored by the fact that credits generated from renewable-powered methods account for 84% of CDR credit purchases, highlighting their market impact. The incorporation of artificial intelligence and data analytics is further improving project planning and operational efficiency, enabling groups to optimize resource use and enhance sustainability. As the demand for power resilience increases, collaborative efforts among stakeholders—including local governments, private companies, and residents—in community energy development are likely to expand.
This trend will pave the way for more inclusive and impactful community energy development initiatives.
The potential for solar photovoltaic (PV) growth is particularly noteworthy, with projections indicating that if solar deployment reaches 800 GW by 2030, it could result in a 20% reduction in coal-fired power generation in China. Furthermore, the globe is anticipated to possess a production capability of over 1,200 GW of solar panels annually by the decade's conclusion, highlighting the scalability of solar solutions in local projects. With renewables expected to contribute 80% of new power generation capacity by 2030, and solar accounting for more than half of this expansion, the emphasis on innovation in community energy development solutions is not only timely but essential for achieving sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Community energy development empowers local populations to harness renewable resources, enhancing resilience and reducing reliance on external energy sources. The swift rise in renewable projects highlights the economic and environmental benefits, including job creation and local investment.
However, challenges such as regulatory hurdles, funding limitations, and the need for community engagement must be effectively addressed to ensure the success of these initiatives. Strategic collaboration, transparent communication, and innovative funding solutions are essential for overcoming these obstacles. The expected support from initiatives like the Inflation Reduction Act’s Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund can further advance community energy efforts.
Looking ahead, technological advancements promise a bright future for community energy. The adoption of energy storage solutions and smart grid technologies will improve the efficiency of local energy systems, while artificial intelligence will enhance project planning and operations. As the emphasis on renewable energy sources grows, community-driven projects will play a crucial role in the transition to a sustainable energy future.
In summary, community energy development is vital for creating sustainable and resilient local economies. By empowering communities to manage their energy resources, these initiatives address both climate change and social equity, fostering a transformative impact. Engaging in this process is essential for communities aiming to thrive in an evolving energy landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is community energy development?
Community energy development includes initiatives that empower populations to produce, manage, and utilize power resources sustainably, primarily focusing on renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and biomass.
What are the goals of community energy development initiatives?
The goals are to strengthen community resilience, reduce reliance on external suppliers, tackle economic and environmental issues specific to geographic regions, and advance sustainable development.
What recent trends are observed in community energy development?
A significant trend is the rise in regional renewable initiatives, with a new solar project being set up every 39 seconds in 2023, indicating increased participation and potential economic benefits.
How do community energy development initiatives impact local economies?
These initiatives promote economic development, generate employment, and encourage investment in nearby areas, which can lead to job creation and improved local economies.
What challenges do community energy development initiatives face?
Challenges include the contraction in heat pump sales in key markets, highlighting the need for consistent policy support and alternative business models to enhance renewable heat deployment.
What is the prediction for community energy development initiatives in 2024?
There is an expected sustained focus on strengthening neighborhoods, especially in light of anticipated increases in heat-related emissions, emphasizing the need for enhanced renewable heat deployment.
What benefits do collective power projects offer?
Collective power projects promote economic development, generate employment, and encourage environmental sustainability by improving local revenue retention and creating green jobs in the renewable energy sector.
How do community energy development initiatives support low-income and Tribal communities?
Programs have allocated significant capacity for low-income areas and Indian lands, ensuring equitable access to power and providing financial benefits such as a minimum 20% bill credit discount for eligible low-income households.
What are the broader impacts of community energy development initiatives?
These initiatives help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve energy efficiency, foster collaboration among residents and organizations, and promote a more sustainable and inclusive future.
List of Sources
- Defining Community Energy Development: An Overview
- Global overview – Renewables 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/renewables-2024/global-overview)
- Solar Market Insight Report – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/us-solar-market-insight)
- The Benefits of Community Energy Initiatives for Local Communities
- home.treasury.gov (https://home.treasury.gov/news/featured-stories/analysis-of-the-first-year-of-the-low-income-communities-bonus-credit-program-building-an-inclusive-and-affordable-clean-energy-economy)
- Advancing Economic Diversification in America’s Energy Communities: Energy Communities IWG Progress Report - Energy Communities (https://energycommunities.gov/progress-report-2024)
- Exploring Different Models of Community Energy Projects
- Statistical evidence for the contribution of citizen-led initiatives and projects to the energy transition in Europe - Scientific Reports (https://nature.com/articles/s41598-023-28504-4)
- arcadia.com (https://arcadia.com/blog/community-solar-statistics)
- Challenges and Keys to Success in Community Energy Development
- US Clean Power Development Sees Record Progress, As Well As Stronger Headwinds (https://wri.org/insights/clean-energy-progress-united-states)
- Global overview – Renewables 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/renewables-2024/global-overview)
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- Future Trends in Community Energy Development
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- The energy world is set to change significantly by 2030, based on today’s policy settings alone - News - IEA (https://iea.org/news/the-energy-world-is-set-to-change-significantly-by-2030-based-on-today-s-policy-settings-alone)




