Overview
Utility-scale renewable planning involves a comprehensive understanding of foundational resources, regulatory frameworks, environmental considerations, and technology integration to ensure successful project development. The article outlines essential tools and strategies, such as the Butte Utility-Scale Solar Guide and GIS mapping tools, while emphasizing the importance of community engagement and innovative technologies in navigating regulatory processes and enhancing project viability.
Introduction
The transition to utility-scale renewable energy projects presents developers with both significant opportunities and formidable challenges. To navigate this complex landscape effectively, a comprehensive understanding of essential resources, regulatory frameworks, and environmental considerations is crucial. This article delves into the foundational tools and strategies necessary for successful project development, including:
- The importance of community engagement
- Innovative technologies
- Strategic planning
By examining case studies of successful projects and the integration of energy storage solutions, this exploration aims to illuminate best practices that can drive the renewable energy sector forward, ultimately contributing to a sustainable energy future.
Foundational Resources for Utility-Scale Renewable Energy Development
To successfully navigate the landscape of utility-scale renewable energy projects, developers should become well-acquainted with several key foundational resources:
- Butte Utility-Scale Solar Guide: This comprehensive guide serves as an essential reference for solar development, detailing critical aspects such as site selection, design parameters, and operational considerations. By following its frameworks, developers can enhance their project outcomes and streamline regulatory compliance for utility-scale renewable planning.
- Renewable Energy Development Atlas: This atlas is an invaluable asset for pinpointing optimal locations for renewable energy initiatives. It offers comprehensive information on land use patterns, ecological constraints, and existing infrastructure, assisting developers in making informed choices that align with utility-scale renewable planning objectives.
- GIS Mapping Tools: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a vital role in analyzing spatial data, which is crucial for site evaluations and planning. By utilizing GIS tools, developers can optimize layouts and enhance site feasibility evaluations based on geographical and environmental factors relevant to utility-scale renewable planning.
- Industry Networks and Associations: Engaging with industry organizations such as the Solar Energy Industries Association is beneficial for developers. These networks provide valuable opportunities for collaboration, knowledge sharing, and access to industry best practices that can guide utility-scale renewable planning.
In addition to these resources, developers should consider the projected utility-scale CAPEX in 2050, which is expected to be $0.90/W. This financial context is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Furthermore, the case study titled "Market Value of Solar Power" highlights that in 2023, solar power's average market value varied significantly across different regions, with the lowest in CAISO at $27/MWh and the highest in ERCOT at $67/MWh.
Projects built in 2022 provided an average of $15/MWh more market value than their costs, contributing to a total of $1.1 billion in benefits. Lastly, as noted by Lazard, the ratio of operational and maintenance costs to CAPEX costs is 1.0:100, emphasizing the importance of considering these factors in financial planning.
Navigating Regulatory Frameworks and Permitting for Renewable Projects
Navigating the regulatory frameworks and permitting processes for renewable energy initiatives requires careful attention to several essential steps:
-
Understanding State and Federal Guidelines: It is crucial to familiarize yourself with the regulatory landscape, including guidelines from agencies such as the Virginia Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) and federal regulations from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This foundational knowledge assists in aligning proposals with existing legal requirements.
- Pre-Application Consultation: Engaging with regulatory agencies early in the permitting process can significantly streamline timelines. Consultations allow developers to gain insights into specific agency requirements and potential hurdles, paving the way for more efficient approvals.
- Preparing Required Documentation: Thorough preparation of necessary paperwork—including impact assessments, plans, and compliance reports—is imperative. Comprehensive documentation not only facilitates the permitting process but also demonstrates a commitment to regulatory adherence and environmental stewardship.
-
Public Involvement: Recognizing the importance of public engagement in the permitting process is vital. Community support can greatly influence project approval outcomes, and proactive outreach efforts can build trust and address public concerns, enhancing the project's overall viability. For example, Greece's program to provide grants of up to 60% for farmers to install solar PV systems illustrates how public engagement can promote sustainable power adoption.
- Monitoring Changes in Regulations: The sustainable power sector is dynamic, with regulations frequently evolving. Staying informed about changes—such as those anticipated in 2024—enables developers to adapt their strategies accordingly and remain compliant with current standards. Significantly, the Ministry of Mineral Resources and Power in South Africa is initiating a seventh round of the REIPPPP, anticipating the allocation of 1.8 GW of solar PV capacity, emphasizing the continuous advancements in the sector.
By adhering to these essential steps and remaining informed about changes in regulatory frameworks, land acquisition specialists can efficiently manage the intricacies related to sustainable resource permitting. As Joseph Womble noted, analyses indicate that to achieve U.S. greenhouse gas reduction targets, annual installation rates of renewables must nearly double those seen in 2023, underscoring the urgency of these efforts.
Environmental Considerations in Utility-Scale Renewable Energy Planning
Key environmental considerations for renewable energy projects encompass several critical areas:
- Carrying out Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): It is crucial to assess the possible effects of sustainable power initiatives on local ecosystems, wildlife, and land use. This process not only identifies adverse effects but also facilitates the development of strategies to mitigate these impacts effectively. Recent assessments have highlighted the importance of understanding the ecological ramifications, particularly regarding the effects of wind turbines on birdlife, as discussed in the International Nuclear Information System in 1993. According to Hailong Zhao, a data curation specialist, "Effective data management is essential for comprehending and reducing the effects of renewable energy initiatives."
- Collaboration with Agencies: Engaging with ecological agencies and stakeholders is paramount to ensure compliance with regulations and to foster coordinated planning efforts. Successful collaboration can significantly enhance project outcomes. For instance, a study published in Wind Engineering in 1990 examined the ecological and community impacts of wind energy in the UK, illustrating the benefits of joint efforts between developers and regulatory bodies.
- Mitigation Strategies: Developing comprehensive strategies to reduce ecological impacts is crucial. This may include habitat restoration initiatives and conservation measures tailored to protect local wildlife. A significant case study published in Renewable Energy in 2000, titled 'Life Cycle Assessment of a Wind Farm and Related Externalities,' evaluated the externalities linked to a wind farm and offered insights into effective mitigation practices that can be implemented across initiatives. Furthermore, the application of particle swarm optimization (PSO) techniques in four recent studies illustrates a quantitative approach to improving the efficiency of impact assessments.
- Sustainability Practices: Integrating optimal methods for sustainability is essential in the construction and operation of alternative power initiatives. This includes utilizing sustainable materials and minimizing resource consumption, which not only reduces environmental footprints but also aligns with broader sustainability goals.
By addressing these factors, sustainable initiatives can achieve a balance between development and ecological integrity, ensuring a positive effect on the environment and the communities they support.
Integrating Renewable Energy Technologies and Storage Solutions
Incorporating sustainable energy technologies is a complex process that necessitates careful consideration of various elements to ensure success. The following key aspects are essential:
-
Choosing the Right Technology: Assessing the suitability of different renewable technologies, such as solar photovoltaic (PV), wind turbines, and hydroelectric systems, is crucial.
Each technology presents unique benefits and challenges that should align with project goals and regional characteristics.
-
Power Storage Solutions: Incorporating power storage systems, including lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro storage, significantly enhances reliability by managing supply fluctuations.
Recent advancements in storage solutions are vital as the global landscape evolves toward greater reliance on intermittent sources like wind and solar.
For example, Deloitte highlights that the year 2025 will signify a crucial moment in tackling the growing gap between clean power supply and demand.
As such, strategic investments in power storage are increasingly important.
-
Smart Grid Integration: The integration of smart grid technologies provides a pathway to optimize resource management and enhance efficiency in distribution.
These technologies facilitate better communication between producers and consumers, enabling a more responsive system that can dynamically adjust to changes in demand and supply, addressing challenges such as frequency and voltage fluctuations.
With Italy’s Enel Group deploying smart meters to over 40 million households, the impact of smart grid technologies on power distribution efficiency is already being realized.
Furthermore, ongoing developments in grid integration technologies are crucial for improving transmission and distribution, particularly in overcoming frequency and voltage challenges.
-
Innovative Approaches: Staying abreast of emerging technologies and innovative practices is essential for improving project outcomes.
Examples include floating solar panels, which maximize space on water bodies, and vertical wind turbines, which can be more effective in urban settings.
As the sector advances, improvements in grid integration technologies will further enhance the reliability and efficiency of sustainable power systems.
Furthermore, state policies, including 100% clean power requirements, play a vital role in unlocking sustainable commitments and supporting data center expansion.
The case study on flexibility requirements in power systems illustrates the urgency of developing more adaptable power frameworks, with over 1 TW of wind and solar installations expected globally.
Beginning in 2025, transmission system operators will evaluate flexibility requirements, prompting large-scale storage acquisitions, thereby emphasizing the essential role of these technologies in the future of sustainable power.
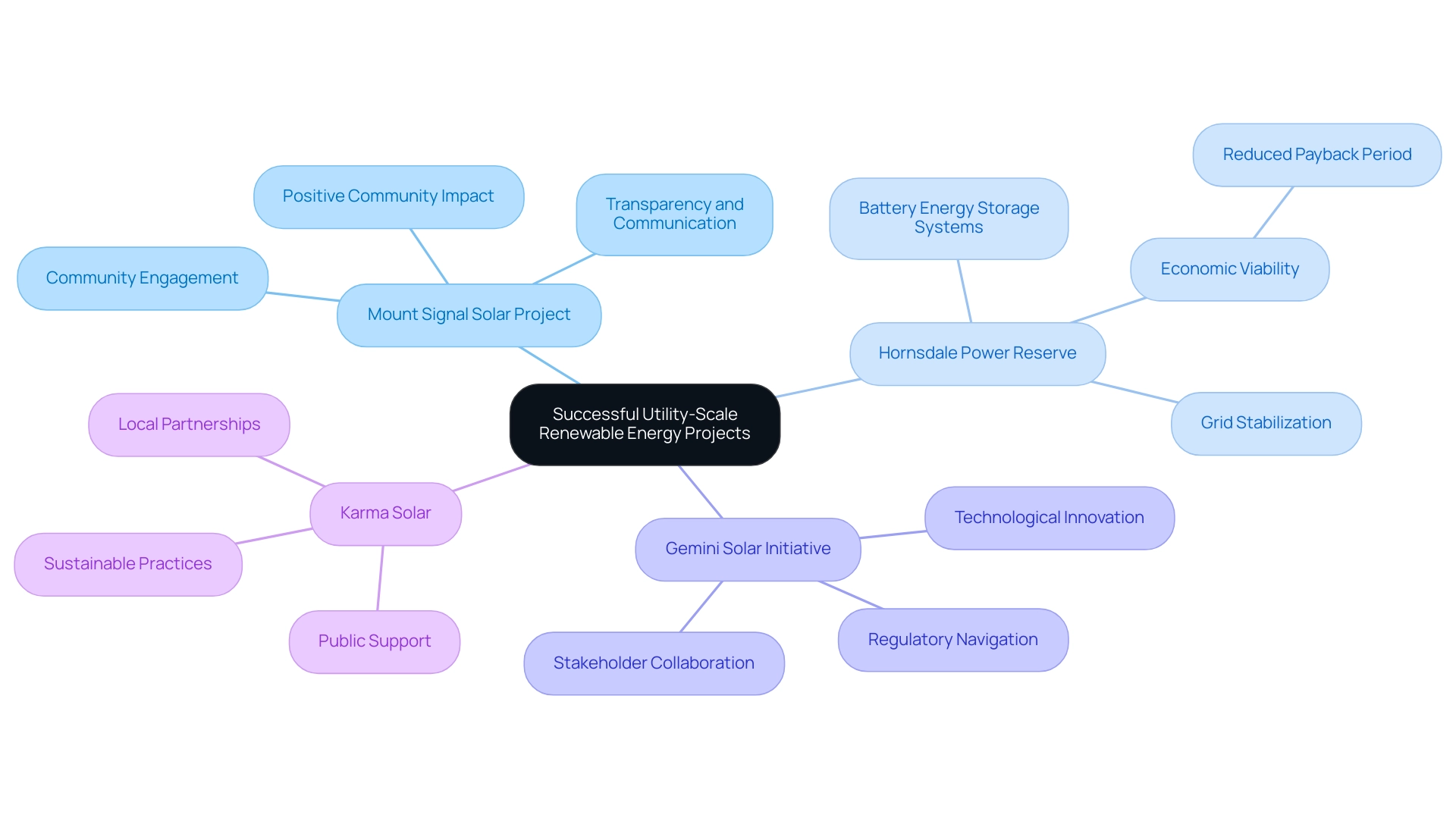
Case Studies: Successful Utility-Scale Renewable Energy Projects
Multiple significant case studies demonstrate the best practices in sustainable land acquisition and management.
-
Mount Signal Solar Project: Situated in California, this solar initiative exemplifies effective site selection coupled with robust community engagement. By proactively involving local stakeholders during the permitting process, the initiative secured necessary approvals and fostered a positive impact within the community.
This approach not only streamlined operations but also enhanced local support, demonstrating the importance of transparency and communication in renewable energy endeavors.
-
Hornsdale Power Reserve: Situated in Australia, this pioneering wind and battery storage initiative highlights the significant advantages of integrating storage solutions. Notably, the integration of Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESs) has been shown to reduce payback periods from over 20 years to approximately 15–18 years in Tennessee, underscoring the economic viability of such initiatives.
Hornsdale serves as a benchmark for future endeavors aiming to balance supply and demand, contributing to stabilizing the grid and promoting a shift toward renewable resources.
-
Gemini Solar Initiative: This endeavor stands out for its innovative technological applications and effective stakeholder collaboration. By addressing environmental concerns upfront and fostering partnerships, the Gemini Solar Project succeeded in navigating complex regulatory landscapes, ultimately achieving a successful outcome that sets a precedent for similar initiatives.
-
Karma Solar: A community-driven initiative, Karma Solar underscores the significance of public support and local partnerships in overcoming regulatory challenges. By prioritizing the needs and concerns of the community, this initiative was able to achieve its goals while ensuring sustainable practices were maintained throughout its lifecycle.
These case studies collectively emphasize the critical role of community engagement, innovative technologies, and utility-scale renewable planning in successfully implementing renewable energy initiatives. As Joseph Womble notes, analyses indicate that to achieve U.S. greenhouse gas reduction targets, annual installation rates of renewables need to nearly double the rates seen in 2023. Therefore, future research should focus on developing interactive tools to visualize the relationships between solar project configurations and their economic feasibility, providing valuable insights for project planning and decision-making.
Conclusion
The exploration of utility-scale renewable energy projects reveals a complex interplay of opportunities and challenges that developers must navigate to achieve success. Understanding foundational resources such as:
- Comprehensive guides
- Renewable energy development tools
- Industry networks
is vital for informed decision-making and efficient project execution. These resources not only facilitate compliance with regulatory frameworks but also promote strategic planning that aligns with sustainability goals.
Moreover, the importance of environmental considerations cannot be overstated. Conducting thorough environmental impact assessments and collaborating with regulatory agencies ensures that projects are designed with ecological integrity in mind. The case studies highlighted demonstrate that:
- Community engagement
- Innovative technologies
- Effective stakeholder collaboration
are essential components that lead to successful project implementation.
As the renewable energy sector evolves, the integration of advanced technologies and energy storage solutions will play a crucial role in enhancing project viability and reliability. The strategic incorporation of smart grid technologies will further optimize energy management, paving the way for a more resilient energy future.
In conclusion, the path toward a sustainable energy future hinges on the ability of developers to leverage key resources, engage communities, and adopt innovative practices. By prioritizing these elements, the renewable energy sector can not only meet growing energy demands but also contribute significantly to global efforts aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The time to act is now, as the collective efforts of developers, regulators, and communities will shape the landscape of renewable energy for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What foundational resources should developers be familiar with for utility-scale renewable energy projects?
Developers should become well-acquainted with the Butte Utility-Scale Solar Guide, Renewable Energy Development Atlas, GIS Mapping Tools, and industry networks and associations like the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA).
What is the purpose of the Butte Utility-Scale Solar Guide?
The Butte Utility-Scale Solar Guide serves as a comprehensive reference for solar development, covering site selection, design parameters, and operational considerations to enhance project outcomes and streamline regulatory compliance.
How does the Renewable Energy Development Atlas assist developers?
The Renewable Energy Development Atlas helps developers identify optimal locations for renewable energy projects by providing information on land use patterns, ecological constraints, and existing infrastructure.
What role do GIS Mapping Tools play in renewable energy project planning?
GIS Mapping Tools are essential for analyzing spatial data, aiding in site evaluations and planning, and allowing developers to optimize layouts based on geographical and environmental factors.
Why should developers engage with industry networks and associations?
Engaging with industry networks and associations like SEIA provides developers with opportunities for collaboration, knowledge sharing, and access to industry best practices that can guide utility-scale renewable planning.
What is the projected utility-scale CAPEX in 2050?
The projected utility-scale CAPEX in 2050 is expected to be $0.90/W.
How did solar power's market value vary in 2023?
In 2023, solar power's average market value varied by region, with the lowest in CAISO at $27/MWh and the highest in ERCOT at $67/MWh.
What financial benefits did projects built in 2022 provide?
Projects built in 2022 provided an average of $15/MWh more market value than their costs, contributing to a total of $1.1 billion in benefits.
What is the importance of the ratio of operational and maintenance costs to CAPEX costs?
The ratio of operational and maintenance costs to CAPEX costs is 1.0:100, highlighting the significance of considering these factors in financial planning for renewable energy projects.
What are the essential steps for navigating regulatory frameworks and permitting processes?
Essential steps include understanding state and federal guidelines, engaging in pre-application consultations, preparing required documentation, recognizing the importance of public involvement, and monitoring changes in regulations.
List of Sources
- Foundational Resources for Utility-Scale Renewable Energy Development
- Utility-Scale PV | Electricity | 2024 | ATB | NREL (https://atb.nrel.gov/electricity/2024/utility-scale_pv)
- Utility-Scale Solar | Energy Markets & Policy (https://emp.lbl.gov/utility-scale-solar)
- Navigating Regulatory Frameworks and Permitting for Renewable Projects
- Global Overview | Policy (https://ren21.net/gsr-2024/modules/global_overview/02_policy)
- Key findings – State of Energy Policy 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/state-of-energy-policy-2024/key-findings)
- US Clean Power Development Sees Record Progress, As Well As Stronger Headwinds (https://wri.org/insights/clean-energy-progress-united-states)
- Environmental Considerations in Utility-Scale Renewable Energy Planning
- sciencedirect.com (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772783124000566)
- sciencedirect.com (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S095965262203921X)
- Impacts and Viability of Solar, Wind, and Electric Vehicles | Sabin Center for Climate Change Law (https://climate.law.columbia.edu/content/impacts-and-viability-solar-wind-and-electric-vehicles)
- Integrating Renewable Energy Technologies and Storage Solutions
- Top 10 Emerging Trends in Renewable Energy Technology (https://energyevolutionexpo.com/trends-in-renewable-energy-technology)
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- Top 10 Renewable Energy Trends in 2025 | StartUs Insights (https://startus-insights.com/innovators-guide/top-10-renewable-energy-trends-2022)
- TOP 10 Trends in Clean Energy Technology in 2024 - S&P Global Commodity Insights (https://press.spglobal.com/2024-01-22-TOP-10-Trends-in-Clean-Energy-Technology-in-2024-S-P-Global-Commodity-Insights)
- Case Studies: Successful Utility-Scale Renewable Energy Projects
- Toward a Comprehensive Economic Comparison Framework for Solar Projects: A Case Study of Utility and Residential Scales (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/23/10320)
- US Clean Power Development Sees Record Progress, As Well As Stronger Headwinds (https://wri.org/insights/clean-energy-progress-united-states)




